High-Risk Areas
The Code of Practice for Agricultural Environmental Management (AEM Code) takes a risk-based approach, where requirements are based on environmental risk. The AEM Code identifies high-risk areas as those with high precipitation (receive 600 mm or more of precipitation), areas over vulnerable aquifers (groundwater vulnerable to contamination) and areas that are phosphorus-affected (surface water bodies that may be impacted by high levels of phosphorus). An agricultural operation could be in one or more of these areas.
While all agricultural operations need to achieve a basic level of protection, operations in high-risk areas need to take more protective measures. For example, some operators in high-risk areas may need to prepare and implement a nutrient management plan.
High-risk conditions are also defined - such as strong winds, intense rainfall, or sloping fields. Additional protective measures are required when these conditions exist, as noted in the specific activity-based requirements.
Interactive Maps
Vulnerable Aquifer Recharge Areas & Phosphorus-Affected Areas Maps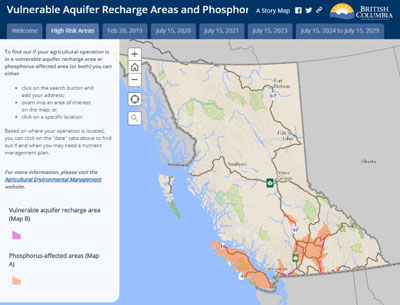
Vulnerable aquifer recharge areas refer to areas where surface water may infiltrate the ground to reach an aquifer that
- is vulnerable to pollution or contamination, or
- is at risk of being adversely affected by nitrates.
A phosphorus-affected area refers to land that drains into surface water bodies that have been or may be adversely affected by high levels of phosphorus.
Click the image to access the interactive map →
High Precipitation Areas Map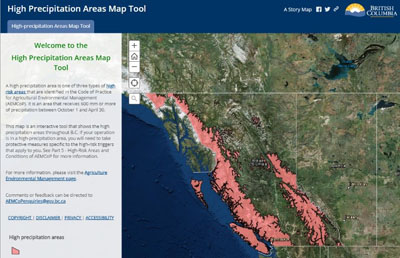
A high-precipitation area is an area in the province that receives 600 mm or more of precipitation between October 1 and April 30.
Click the image to connect to the interactive map →
Printable Maps of High-Risk Areas
High-resolution maps of high-risk areas are available for digital download and printing.
