Ankle Injury - X-Ray for Acute Injury of the Ankle or Mid-Foot
Effective Date: March 15, 2014
Recommendations and Topics
Scope
This guideline makes recommendations for adults aged ≥ 19 years with acute ankle and mid-foot injuries, presenting for the first time in a clinical setting (emergency department and primary care). This guideline excludes recommendations for patients younger than 19 years, with multiple painful injuries, pregnant, cognitively impaired or with sensory deficits in their lower extremities.
Key Recommendations
- Use the Ottawa Ankle Rules (OAR) to exclude fractures and reduce unnecessary imaging.1-3
- Advise patients to seek follow-up care if their pain or ability to bear weight has not improved in five to seven days.4
Diagnosis
Historically imaging is ordered for most patients presenting with an ankle and/or mid-foot injury even though only about 15% have clinically significant fractures.1-3
This guideline recommends the use of the OAR when diagnosing ankle and mid-foot fractures and to reduce unnecessary imaging.1-7
Screening
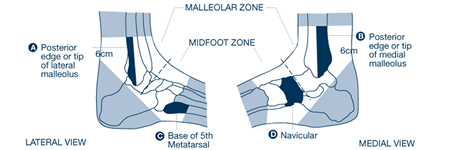
Ankle x-rays are required only if there is pain in the malleolar zone (refer to Figure 1) as well as any one of:
- Bone tenderness at A; or
- Bone tenderness at B; or
- Inability to bear weight both immediately and in the clinical setting (unable to take four steps independently, even if limping).
Foot x-rays are required only if there is pain in the mid-foot zone (refer to Figure 1) as well as any one of:
- Bone tenderness at C; or
- Bone tenderness at D; or
- Inability to bear weight both immediately and in the clinical setting (unable to take four steps independently, even if limping).
Whether or not an x-ray is ordered, it is recommended that the patient seek follow-up care if their pain or ability to bear weight has not improved in five to seven days.
Figure 1: Zones of the Ankle and Mid-Foot According to the Ottawa Ankle Rules4
Resources
References
- Anis AH, Stiell IG, Stewart DG, Laupacis A. Cost-effectiveness analysis of the Ottawa Ankle Rules. Ann Emerg Med. 1995;26(4):422-8.
- Jenkin M, Sitler MR, Kelly JD. Clinical usefulness of the Ottawa Ankle Rules for detecting fractures of the ankle and midfoot. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):480-2.
- Polzer H, Kanz KG, Prall WC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of acute ankle injuries: development of an evidence-based algorithm. Orthop Rev. 2012;4(e5):22-32.
- Stiell I, McKnight RD, Greenburg GH, et al. Implementation of the Ottawa Ankle Rules. JAMA. 1994;271:827-32.
- Seah R, Mani-Babu S. Managing ankle sprains in primary care: what is best practice? A systematic review of the last 10 years of evidence. Br Med Bull. 2011;97:105-35.
- Tiemstra JD. Update on acute ankle sprains. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85(12):1170-6.
- Stiell I, Wells G, Laupacis A, et al. Multicentre trial to introduce the Ottawa Ankle Rules for use of radiography in acute ankle injuries. BMJ. 1995;311:594-7.
Resources
- The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, www.ohri.ca/emerg/cdr/ankle.html - provides the OAR in various printable formats.
- HealthLink BC, www.healthlinkbc.ca – provides information for patients on toe, foot and ankle injuries.
Diagnostic codes
845 sprains and strains of ankle and foot
824 ankle fracture
This guideline is based on scientific evidence current as of the Effective Date.
This guideline was developed by the Guidelines and Protocols Advisory Committee, approved by the British Columbia Medical Association and adopted by the Medical Services Commission.
|
The principles of the Guidelines and Protocols Advisory Committee are to:
|
Disclaimer The Clinical Practice Guidelines (the "Guidelines") have been developed by the Guidelines and Protocols Advisory Committee on behalf of the Medical Services Commission. The Guidelines are intended to give an understanding of a clinical problem and outline one or more preferred approaches to the investigation and management of the problem. The Guidelines are not intended as a substitute for the advice or professional judgment of a health care professional, nor are they intended to be the only approach to the management of clinical problems. We cannot respond to patients or patient advocates requesting advice on issues related to medical conditions. If you need medical advice, please contact a health care professional.


 TOP
TOP TOP
TOP