3 - Cardiovascular disease and disorder - CCMTA Medical Standards
Cardiovascular disease and disorder and medical fitness to drive.
- 3.6.1 Congenital heart defects
- 3.6.2 Acute Coronary Syndromes – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.3 Acute Coronary Syndromes – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.4 Asymptomatic coronary artery disease or stable angina
- 3.6.5 CABG surgery – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.6 CABG surgery – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.7 Premature atrial or ventricular contractions
- 3.6.8 Ventricular fibrillation with no reversible cause – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.9 Ventricular fibrillation with no reversible cause – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.10 Hemodynamically unstable VT – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.11 Hemodynamically unstable VT – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.12 Sustained VT and an LVEF of <35% – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.13 Sustained VT and an LVEF of <35% Commercial drivers
- 3.6.14 Sustained VT and an LVEF of equal or greater than 35% Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.15 Sustained VT and an LVEF of equal or greater than 35% Commercial drivers
- 3.6.16 Non sustained VT
- 3.6.17 Paroxysmal SVT, AF or AFL with no impaired consciousness
- 3.6.18 Paroxysmal SVT, AF or AFL with impaired consciousness
- 3.6.19 Persistent or permanent paroxysmal SVT, AF or AFL
- 3.6.20 Sinus node dysfunction
- 3.6.21 Atrioventricular (AV) or intraventricular block – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.22 Atrioventricular (AV) or intraventricular block – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.23 Permanent pacemakers – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.24 Permanent pacemakers – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.25 Declined an ICD or have an ICD implanted as primary prophylaxis – Non- commercial drivers
- 3.6.26 Declined an ICD or have an ICD implanted as primary prophylaxis - Commercial drivers
- 3.6.27 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for sustained VT – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.28 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for sustained VT – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.29 ICD therapy (shock or ATP) has been delivered – Non-Commercial drivers
- 3.6.30 ICD therapy (shock or ATP) has been delivered – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.31 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for VF or VT – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.32 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for VF or VT – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.33 Inherited heart disease – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.34 Inherited heart disease – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.35 Medically treated valvular heart disease – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.36 Medically treated aortic stenosis or aortic sclerosis – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.37 Medically treated aortic or mitral regurgitation or mitral stenosis – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.38 Surgically treated valvular heart disease – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.39 Surgically treated valvular heart disease – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.40 Mitral valve prolapse – All drivers
- 3.6.41 Congestive heart failure – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.42 Congestive heart failure – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.43 Left ventricular dysfunction or cardiomyopathy – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.44 Left ventricular dysfunction or cardiomyopathy – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.45 Heart transplant – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.46 Heart transplant – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.47 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy – Non-commercial drivers
- 3.6.48 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy – Commercial drivers
- 3.6.49 Syncope
- 3.6.50 CCS recommendations regarding transient conditions (Waiting Periods)
3.1 About cardiovascular disease
Overview
Cardiovascular disease is an umbrella term used to describe a variety of disorders relating to the heart and blood vessels.
Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease, which is also called coronary, ischemic or atherosclerotic heart disease, is characterized by the presence of atherosclerosis in the arteries of the heart.
Atherosclerosis is the progressive buildup of fatty deposits called plaque, which narrows the coronary arteries and reduces blood flow to the heart. Complications of coronary artery disease include:
- angina (pain or discomfort due to lack of oxygen to the heart muscle)
- myocardial infarction (heart attack), and
- ischemic cardiomyopathy (permanent damage to the heart muscle).
Disturbances of cardiac rhythm
Disturbances of cardiac rhythm, or arrhythmias, include:
- tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
- bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- fibrillation or flutter (abnormal twitching of the heart muscle), and
- heart block.
These arrhythmias may arise from the heart muscle itself or the conduction system and are often secondary to underlying heart disease.
Valvular heart disease
Disease affecting the heart valves may result in stenosis and regurgitation, and is associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism.
In valvular stenosis, the valve opening is smaller than normal due to hardening or fusing of the valve’s leaflets. This may cause the heart to have to work harder to pump blood through the valves. In valvular regurgitation or “leaky valve”, the valve does not close tightly enough, allowing some blood to leak backwards across the valve. As the leak worsens, the heart has to work harder to make up for the leaky valve, and less blood may flow to the rest of the body. Stenosis and regurgitation may coexist.
Individuals who have undergone valve replacement surgery are subject to a certain irreducible incidence of late complications such as thromboembolism, dehiscence, infection and mechanical malfunction.
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure usually is a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart is unable to pump the quantity of blood required to meet the body's needs. It is generally the result of heart disease but may be secondary to non-cardiac conditions such as fluid overload and anemia.
The severity of congestive heart failure can be assessed by measuring the fraction of blood being pumped out of the left ventricle with each beat. This is expressed as a ratio called the left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF). Healthy individuals generally have an LVEF greater than 55%.
The New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification system provides a simple, clinical measure for assessing the degree of heart failure. This system describes the effect of cardiovascular disease on an individual’s general physical activity, according to the categories shown in the following table.
| Category | Description |
| I | No symptoms and no limitation in ordinary physical activity. Comfortable at rest. |
| II | Mild symptoms and slight limitation during ordinary activity. Comfortable at rest. |
| III | Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms, even during less-than- ordinary activity. Comfortable only at rest. |
| IV | Severe limitations. Experiences symptoms even while at rest. |
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy refers to a change in the size, strength or flexibility in the heart muscle. These changes can reduce the amount of blood being pumped out of the heart, and may lead to congestive heart failure. Cardiomyopathy is associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias.
3.2 Prevalence
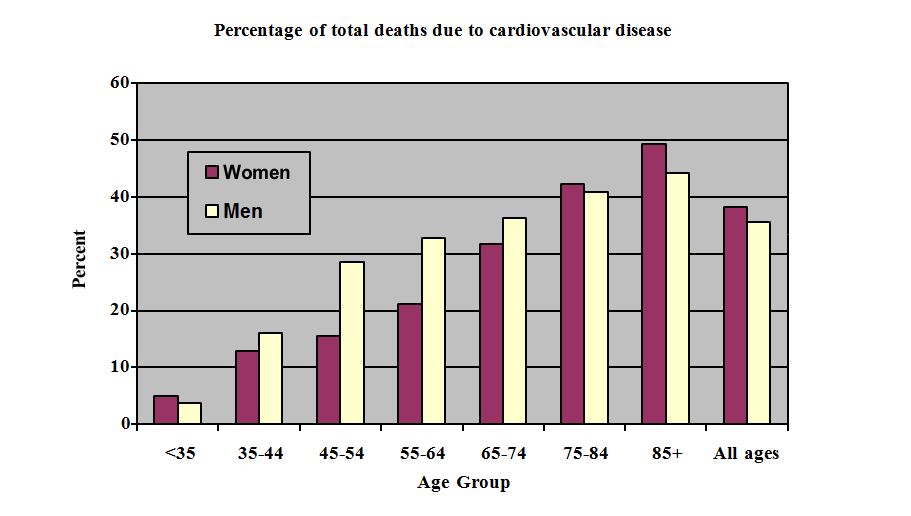
Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of death, disability and health care costs in Canada. Although cardiovascular disease death rates have been declining since the mid- 1960s, statistics from 1997 indicate that cardiovascular disease was still the leading cause of death in Canada, accounting for 36% of all deaths in men and 38% in women. As shown in the graph below, the proportion of deaths caused by cardiovascular disease increases dramatically with age.
3.3 Cardiovascular disease and adverse driving outcomes
Research indicates that drivers with cardiovascular disease as a whole have a higher risk for adverse driving outcomes than those without cardiovascular disease. However, there is relatively little research on the effects of specific cardiovascular disorders and driving outcomes.
3.4 Effect of cardiovascular disease on functional ability to drive
| Condition | Type of driving impairment and assessment approach4 | Primary functional ability affected | Assessment tools |
|
Coronary artery disease Arrhythmias Valvular heart disease Cardiomyopathy |
Episodic impairment: Medical assessment – likelihood of impairment |
All – sudden incapacitation | Medical assessments |
| Congestive heart failure | Persistent Impairment: Functional assessment |
Can affect Motor Sensory and Cognitive function May also result in general debility or lack of stamina |
Medical assessments Functional Assessment |
|
Episodic impairment: Medical assessment – likelihood of impairment |
All – sudden incapacitation | Medical assessments Specialist’s report | |
|
Post cardiac arrest Post-operative cognitive decline (POCD) |
Persistent Impairment: Functional assessment |
Can affect Motor Sensory and Cognitive function May also result in general debility |
Medical assessments Functional Assessment |
4 See Part 1 for a discussion of the use of functional assessments for driver licensing decisions.
The effect of cardiovascular disease on an individual’s functional ability to drive may be episodic or persistent.
Episodic impairment
The potential episodic impairment is a partial or complete loss of consciousness that incapacitates the driver. This may be caused by a variety of cardiovascular events such as:
- Bradyarrhythmias
- Tachyarrhythmias
- Myocardial disease (massive myocardial infarction)
- Left ventricular myocardial restriction or constriction
- Pericardial constriction or tamponade
- Aortic outflow tract obstruction
- Aortic valvular stenosis, or
- Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
Persistent impairment
Individuals with congestive heart failure may develop persistent cognitive impairment, loss of stamina or general debility as a result of a reduction of oxygen to the brain, organs and tissues. Cardiac arrest also may cause persistent cognitive impairment where a loss of blood to the brain causes brain damage.
Neurocognitive deficits can occur in individuals undergoing intracardiac procedures (e.g. valve surgery) or extracardiac procedures (e.g. coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery). However, the majority of studies investigating cognitive decline have focused on individuals undergoing CABG surgery. The results of those studies indicate that a significant number of individuals experience post-operative cognitive decline (POCD) for several months after surgery, with documented declines in memory, attention, speed of processing, and executive functioning. Studies indicate that between 20% and 79% of individuals experience POCD between 6 weeks and 6 months of CABG surgery, with a majority of the studies showing a rate of 45% or higher. In those studies that have followed individuals for more than 6 months post-surgery, the results indicate that up to 35% of individuals will show POCD one year after surgery. The current understanding is that POCD is the result of a number of factors associated with cardiac treatment, rather than a single factor such as the use of cardiopulmonary bypass.
3.5 Compensation
Individuals with cardiovascular disease are not able to compensate for their functional impairment.
3.6 Guidelines for assessment
These guidelines are based primarily on recommendations contained in the final report of the 2003 Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) Consensus Conference Assessment of the Cardiac Patient for Fitness to Drive and Fly. Additionally, the CCS 2012 Focused Position Statement, Update on Assessment of the Cardiac Patient for Fitness to Drive: Following LVAD Implantation has been incorporated into the B.C. specific guidelines 3.6.43. The CCS recommendations focus exclusively on the potential episodic impairment associated with cardiovascular diseases.
Where the standards differ from the CCS recommendations, the rationale is included in the table.
For CCS recommendations for transient conditions (waiting periods) see Section 3.6.50 which form part of the standards.
3.6.1 Congenital heart defects
| National Standard |
All drivers eligible for a licence if
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
|
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | Congenital heart defects are not specifically addressed in the CCS recommendations. This standard is included here to assist where a congenital heart defect is reported to an authority. The nature of congenital heart defects and their treatment is variable; therefore there are no driver fitness standards specifically for them. |
3.6.2 Acute Coronary Syndromes – Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if
|
| BC Guidelines |
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, or as recommended by the treating physician, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies. |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.3 Acute Coronary Syndromes – Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment, or as recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.4 Asymptomatic coronary artery disease or stable angina
| National Standard | All drivers eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines | RoadSafetyBC will not generally request further information |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine commercial or age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Confirmation that coronary artery disease is asymptomatic or angina is stable |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.5 CABG surgery – Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
|
BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Date of CABG surgery |
| Rationale |
CSS recommendations |
3.6.6 CABG surgery – Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
|
BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment, or as recommended by the treating physician. |
| Information from health care providers | Date of CABG surgery |
| Rationale |
CSS recommendations |
3.6.7 Premature atrial or ventricular contractions
| National Standard |
All drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
|
| Information from health care providers | Confirmation that there is no impaired level of consciousness caused by cerebral ischemia |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.8 Ventricular fibrillation with no reversible cause - Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers who have ventricular fibrillation (VF) with no reversible cause. It does not apply to drivers who have VF due to any of the following reversible causes:
- VF within 24 hours of myocardial infarction
- VF during coronary angiography
- VF with electrocution, or
- VF secondary to drug toxicity.
If VF has a reversible cause, it is considered a transient condition, see 3.6.50.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, or as recommended by the treating physician, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Date of last episode of ventricular fibrillation |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.9 Ventricular fibrillation with no reversible cause – Commercial drivers
This standard applies to commercial drivers who have ventricular fibrillation (VF) with no reversible cause. It does not apply to drivers who have VF due to any of the following reversible causes:
- VF within 24 hours of myocardial infarction
- VF during coronary angiography
- VF with electrocution, or
- VF secondary to drug toxicity.
If VF has a reversible cause, it is considered a transient condition. The CCS recommendation for VF with a reversible cause is included in 3.6.50.
| National Standard | Commercial drivers not eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines | RoadSafetyBC will not generally request further information |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | N/A |
| Reassessment | N/A |
| Information from health care providers | N/A |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.10 Hemodynamically unstable VT – Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years or as recommended by the treating physician, unless routine age re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Whether the underlying condition causing VT has been successfully treated |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.11 Hemodynamically unstable VT – Commercial drivers
| National Standard | Commercial drivers not eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines | RoadSafetyBC will not generally request further information |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | N/A |
| Reassessment | N/A |
| Information from health care providers | N/A |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.12 Sustained VT and a LVEF of <35% - Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers who have sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) with:
- A left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of <35% and
- No associated impaired level of consciousness.
Sustained VT means VT having a cycle length of 500 msec or less, and lasting 30 seconds or more or causing hemodynamic collapse.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
RoadSafetyBC may find individuals fit to drive if:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
RoadSafetyBC will impose the following condition on an individual who has been treated with an ICD and is found fit to drive:
|
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, or as recommended by the treating physician, unless routine commercial or age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale |
CSS recommendations |
3.6.13 Sustained VT and an LVEF of <35% Commercial drivers
This standard applies to commercial drivers who have sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) with:
- A left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of <35% and
- No associated impaired level of consciousness.
Sustained VT means VT having a cycle length of 500 msec or less, and lasting 30 seconds or more or causing hemodynamic collapse.
| National Standard | Commercial drivers not eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines | RoadSafetyBC will not generally request further information |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | N/A |
| Reassessment | N/A |
| Information from health care providers | N/A |
| Rationale |
3.6.14 Sustained VT and an LVEF of equal or greater than 35% Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers who have sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT):
- With a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of equal or greater than 35%, with no associated impaired level of consciousness, and
- For whom an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) has not been recommended.
Sustained VT means VT having a cycle length of 500 msec or less, and lasting 30 seconds or more or causing hemodynamic collapse.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.15 Sustained VT and an LVEF of equal or greater than 35% Commercial drivers
This standard applies to commercial drivers who have sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT):
- With a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of equal or greater than 35%
- With no associated impaired level of consciousness, and
- For whom an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) has not been recommended
Sustained VT means VT having a cycle length of 500 msec or less, and lasting 30 seconds or more or causing hemodynamic collapse.
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.16 Non sustained VT
This standard applies to all drivers who have non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT).
Non-sustained VT means VT having a cycle length of 500 msec or less, and lasting less than 30 seconds without hemodynamic collapse.
| National Standard | All drivers eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines | RoadSafetyBC will not generally request further information |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | If there is no underlying cardiovascular disease, no re-assessment is required, other than routine commercial or age-related re-assessment. Where there is an underlying cardiovascular disease, RoadSafetyBC will re-assess according to the guidelines for that condition |
| Information from health care providers | None |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.17 Paroxysmal SVT, AF or AFL with no impaired consciousness
This standard applies to all drivers who have had paroxysmal:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Atrial fibrillation (AF), or
- Atrial flutter (AFL)
with no associated impaired level of consciousness.
| National Standard | All drivers eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines | RoadSafetyBC will not generally request further information |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in five years. If there have been no further occurrences at that time, no further re-assessment is required, unless routine commercial or age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | None |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.18 Paroxysmal SVT, AF or AFL with impaired consciousness
This standard applies to all drivers who have had paroxysmal:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Atrial fibrillation (AF), or
- Atrial flutter (AFL)
with an associated impaired level of consciousness.
| National Standard |
All drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in five years. If there have been no further occurrences at that time, no further re-assessment is required, unless routine commercial or age-related re-assessment applies. For individuals who have had pacemaker implantation, the re-assessment guidelines under 3.6.23 and 3.6.24 apply |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.19 Persistent or permanent paroxysmal SVT, AF or AFL
This standard applies to all drivers who have persistent or permanent paroxysmal:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Artial fibrillation (AF), or atrial flutter (AFL).
| National Standard |
All drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, or as recommended by the treating physician, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.20 Sinus node dysfunction
| National Standard |
All drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine commercial or age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.21 Atrioventricular (AV) or intraventricular block – Non-commercial drivers
If a permanent pacemaker is implanted, the recommendations in 3.6.23 prevail.
| National Standard |
are eligible for a licence
are eligible for a licence if:
are not eligible for a licence |
|
BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine commercial or age related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.22 Atrioventricular (AV) or intraventricular block - Commercial drivers
If a permanent pacemaker is implanted, the recommendations in 3.6.24 prevail.
| National Standard |
are eligible for a licence
are eligible for a licence if
are not eligible for a licence |
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
Drivers with:
have an annual Holter that shows there is no higher grade AV block. Drivers with a congenital third degree AV block have an annual Hotler that shows no documented pause > 3 seconds |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.23 Permanent pacemakers - Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | No conditions are required |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.24 Permanent pacemakers - Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
Regularly check pacemaker at a pacemaker clinic and do not driver if there is a pacemaker malfunction |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.25 Declined an ICD or have an ICD implanted as primary prophylaxis – Non- commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers who:
- Have had an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) implanted as a primary prophylaxis, or
- Have declined an ICD recommended as primary prophylaxis
When implanted as a primary prophylaxis, the ICD is implanted to prevent sudden cardiac death in individuals considered to be at high risk but who have not had an episode of ventricular arrhythmia.
Individuals whose ICD also regulates pacing for bradycardia must also meet the standard for permanent pacemakers in 3.6.23.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
|
| Reassessment |
If the individual’s condition is controlled and stable, RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless a shorter period is recommended by the treating physician or routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.26 Declined an ICD or have an ICD implanted as primary prophylaxis – Commercial drivers
This standard applies to commercial drivers who:
- Have had an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) implanted as a primary prophylaxis, or
- Have declined an ICD recommended as primary prophylaxis
When implanted as a primary prophylaxis, the ICD is implanted to prevent sudden cardiac death in individuals considered to be at high risk but who have not had an episode of ventricular arrhythmia.
Individuals whose ICD also regulates pacing for bradycardia must also meet the standard for permanent pacemakers in 3.6.24.
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers generally not eligible for a licence. May be eligible if:
|
| BC Guidelines | If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC will request an assessment from a cardiologist |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | No conditions are required |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually |
| Information from health care providers | Cardiologist’s assessment that the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is 1% per CCS recommendation |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation – an ICD may sometimes be implanted in low risk patients. Individual cases may be made for allowing a commercial driver to continue driving with an ICD provided the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is felt to be 1% or less |
3.6.27 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for sustained VT – Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
|
| Reassessment | If the individual’s condition is controlled and stable, RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless a shorter period is recommended by the treating physician or routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.28 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for sustained VT - Commercial drivers
| National Standard | Commercial drivers not eligible for a licence*** |
| BC Guidelines | Commercial drivers generally not eligible for a licence, may be eligible if cardiologist assessment indicates that the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is 1% or less. |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | N/A |
| Reassessment | N/A |
| Information from health care providers | N/A |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation*** |
***Individual cases may be made for allowing a commercial driver to continue driving with an ICD provided the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is felt to be 1% or less.
3.6.29 ICD therapy (shock or ATP) has been delivered - Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers where ICD therapy (shock or ATP) has been delivered and there is an associated impaired level of consciousness, or the therapy delivered by the device was disabling.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | As per the standard for the underlying cardiovascular condition |
| Reassessment | As per the standard for the underlying cardiovascular condition |
| Information from health care providers | Date of the event |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.30 ICD therapy (shock or ATP) has been delivered - Commercial drivers
| National Standard | Commercial drivers are ineligible for a licence*** |
| BC Guidelines |
Commercial drivers generally not eligible for a licence. May be eligible if cardiologist assessment indicates that the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is 1% or less. |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | N/A |
| Reassessment | N/A |
| Information from health care providers | N/A |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation*** |
***Individual cases may be made for allowing a commercial driver to continue driving with an ICD provided the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is felt to be 1% or less.
3.6.31 ICD Implanted as secondary prophylaxis for VF or VT - Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers who have had an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) implanted as a secondary prophylaxis for VF or VT with an impaired level of consciousness.
When implanted as a secondary prophylaxis, the ICD is implanted to prevent sudden cardiac death in individuals who have suffered a cardiac arrest or who suffer from malignant arrhythmias that do not respond readily to medical treatment.
Individuals whose ICD also regulates pacing for bradycardia must also meet the standard for permanent pacemakers in 3.6.23.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
|
| Reassessment |
If the individual’s condition is controlled and stable, RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless a shorter period is recommended by the treating physician or routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Date of last episode of sustained symptomatic VT or syncope judged to be likely due to VT or cardiac arrest |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.32 ICD implanted as secondary prophylaxis for VF or VT – Commercial drivers
| National Standard | Commercial drivers not eligible for a licence*** |
| BC Guidelines |
Commercial drivers generally not eligible for a licence. May be eligible if cardiologist assessment indicates that the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is 1% or less. |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | N/A |
| Reassessment | N/A |
| Information from health care providers | N/A |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation*** |
***Individual cases may be made for allowing a commercial driver to continue driving with an ICD provided the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is felt to be 1% or less.
3.6.33 Inherited heart disease – Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers with the following inherited heart diseases:
- Brugada’s Syndrome
- Long QT Syndrome, and
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy.
| National Standard |
Non-Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines | If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC will request an assessment from a cardiologist |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | No conditions are required |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually or more frequently as recommended by the driver's cardiologist |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.34 Inherited heart disease – Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers generally not eligible for a licence. May be eligible if:
|
| BC Guidelines | If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC will request an assessment from a cardiologist |
| Conditions for maintaining licence | No conditions are required |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually |
| Information from health care providers | Cardiologist’s assessment which indicates that the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is 1% or less |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation – Inherited heart diseases may sometimes be identified to pose a very low risk to patients. Individual cases can sometimes be made to allow a commercial driver to continue to drive despite the diagnosis of one of these diseases, provided the annual risk of sudden incapacitation is believed to be less than one percent |
3.6.35 Medically treated valvular heart disease – Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers with medically treated:
- Aortic stenosis
- Aortic regurgitation
- Mitral stenosis, or
- Mitral regurgitation.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.36 Medically treated aortic stenosis or aortic sclerosis – Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | Have an annual medical follow-up |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.37 Medically treated aortic or mitral regurgitation or mitral stenosis – Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.38 Surgically treated valvular heart disease – Non-commercial drivers
This standard applies to non-commercial drivers with:
- Mechanical prostheses
- Mitral bioprostheses with non-sinus rhythm
- Mitral valve repair with non-sinus rhythm
- Aortic bioprostheses
- Mitral bioprostheses with sinus rhythm, or
- Mitral valve repair with sinus rhythm.
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.39 Surgically treated valvular heart disease – Commercial drivers
This standard applies to commercial drivers with:
- Mechanical prostheses
- Mitral bioprostheses with non-sinus rhythm
- Mitral valve repair with non-sinus rhythm
- Aortic bioprostheses
- Mitral bioprostheses with sinus rhythm, or
- Mitral valve repair with sinus rhythm.
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.40 Mitral valve prolapse – All drivers
| National Standard |
All drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | Where the condition is longstanding and asymptomatic, RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every five years, unless routine commercial or age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Whether the driver is asymptomatic |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.41 Congestive heart failure - Non-commercial drivers
If using left ventricular assist device (LVAD), see 3.6.43
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
RoadSafetyBC may find individuals fit to drive if:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every 5 years or in accordance with routine age-related re-assessment, unless more frequent re-assessment is recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendations |
3.6.42 Congestive heart failure - Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
RoadSafetyBC may find individuals fit to drive if:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment, unless more frequent re-assessment is recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CSS recommendations |
3.6.43 Left ventricular dysfunction or cardiomyopathy – Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
If has left ventricular assist device (LVAD), RoadSafetyBC may find individuals fit to drive if:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | No conditions are required |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every 5 years or in accordance with routine age- related re-assessment, unless more frequent re-assessment is recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation These guidelines are consistent with the 2012 CCS Position Statement Update on Assessment of the Cardiac Patient for Fitness to Drive: Fitness Following Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation |
3.6.44 Left ventricular dysfunction or cardiomyopathy - Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment, unless more frequent re-assessment is recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation These guidelines are consistent with the 2012 CCS Position Statement Update on Assessment of the Cardiac Patient for Fitness to Drive: Fitness Following Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation |
3.6.45 Heart transplant – Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | No conditions are required |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess every 5 years if the individual’s condition is controlled, stable and asymptomatic. Otherwise, RoadSafetyBC will re-assess as recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.46 Heart transplant - Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence |
Have an annual medical follow-up, including a non-invasive test of ischemic burden |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment, unless more frequent re-assessment is recommended by the treating physician |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.47 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - Non-commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Non-commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | None |
| Reassessment |
RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually until the condition is controlled and stable and then every five years, unless routine age-related re-assessment applies |
| Information from health care providers | Whether the driver has had an episode of impaired level of consciousness |
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.48 Hypertrophic cardiomyopthy - Commercial drivers
| National Standard |
Commercial drivers eligible for a licence if:
|
| BC Guidelines |
If further information regarding an individual’s medical condition is required, RoadSafetyBC may request:
|
| Conditions for maintaining licence | Have a annual Holter to test for nonsustained VT |
| Reassessment | RoadSafetyBC will re-assess annually until the condition is controlled and stable and then in accordance with routine commercial re-assessment |
| Information from health care providers |
|
| Rationale | CCS recommendation |
3.6.49 Syncope
The standards for syncope are included in Chapter 19.
3.6.50 CCS recommendations regarding transient conditions (Waiting Periods)
The waiting periods in these recommendations form part of the standard and refer to the time interval following onset of the referenced cardiac condition or event during which it is recommended that an individual does not drive. These standards are intended to mitigate the risk of an episodic impairment of functional ability to drive.
- Recurrence of the referenced cardiac condition or event during a waiting period resets the waiting period.
- If more than one waiting period applies (because of multiple conditions/events) the longer waiting period should be applied, unless otherwise stated.
A. Coronary artery disease
Acute coronary syndromes – waiting periods
| Condition | Classes 5-7 Non commercial | Classes 1-4 Commercial |
| ST elevation MI | 1 month after discharge |
3 months after discharge |
| Non-ST elevation MI with significant LV damage | ||
|
Non-ST elevation MI with minor LV damage If PCI performed during initial hospital stay |
48 hours after PCI | 7 days after PCI |
|
If PCI not performed during initial hospital stay |
7 days after discharge | 30 days after discharge |
|
Acute coronary syndrome without MI (unstable angina) If PCI performed during initial hospital stay |
48 hours after PCI | 7 days after PCI |
|
If PCI not performed during initial hospital stay |
7 days after discharge | 30 days after discharge |
|
Notes: ST elevation: refers to the appearance of the ST segment of an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) MI: Myocardial infarction (heart attack) LV: left ventricle Significant LV damage: any MI which is not classified as minor Minor LV damage: an MI defined only by elevated troponin + ECG changes and in the absence of a new wall motion abnormality. |
||
Stable coronary syndromes – waiting periods
| Non-Commercial | Commercial | |
|
Stable angina |
No restrictions | |
| Asymptomatic coronary artery disease | ||
| PCI | 48 hours after PCI | 7 days after PCI |
|
Notes: PCI: Percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty) |
||
Cardiac surgery for coronary artery disease – waiting periods
| Non-commercial | Commercial | |
| Coronary artery bypass graft | 1 month after discharge | 3 months after discharge |
B. Disturbances of cardiac rhythm, arrhythmia devices and procedures
Catheter ablation and EPS
| Non-commercial | Commercial | |
|
Catheter ablation procedure EPS with no inducible sustained ventricular |
48 hours after discharge | 1 week after discharge |
|
Notes: EPS: electrophysiology |
||
Disturbances of cardiac rhythm and arrhythmia devices
Ventricular arrhythmias
| Non-commercial | Commercial | |
| VF with a reversible cause | No driving until/unless successful treatment of underlying conditions | |
|
Notes: VF: ventricular fibrillation Examples of reversible causes of VF:
|
||
