Text field
A text field enables the user to enter a short amount of text into an interface or form.
On this page:
How to use this component
The text field component enables a user to enter text into an interface. They are commonly used in:
- Forms
- Search interfaces
- Login interfaces
The text field should be used when the user needs to enter a single line of text (for example, their name or email address.) If your use case requires the user to enter multiple lines of text (for example, a comment), use a text area instead.
Text fields are generally used with buttons to submit data into a system.
Structure and behaviour
Anatomy
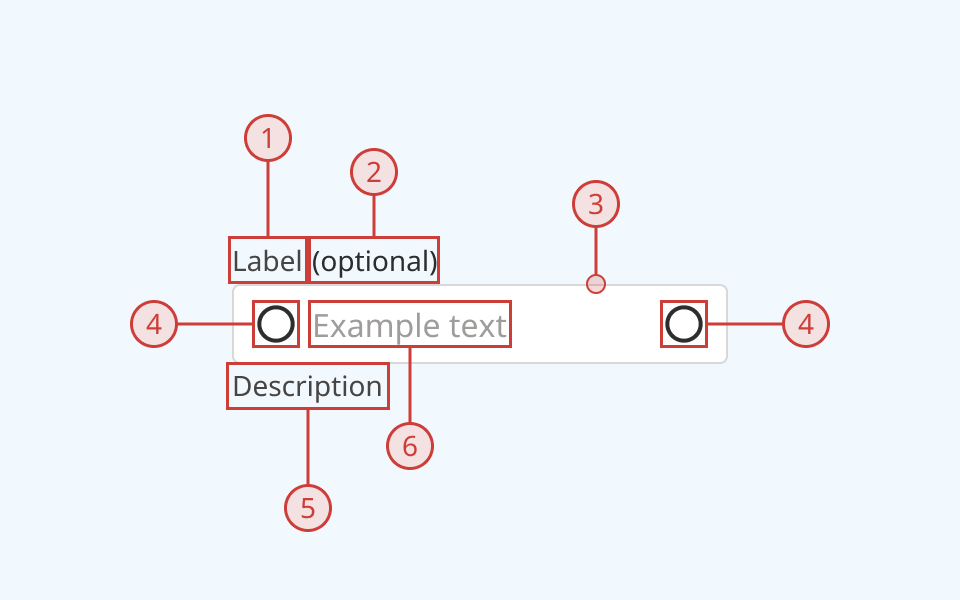
A text field component has:
- A text label, to explain the purpose of the input
- A secondary label, indicating when a selection is required or optional
- A light border around the input field
- Icons, arrayed to the left and/or right of the input box (optional)
- A text description below the input field, to provide additional helper text (optional)
- A text input slot
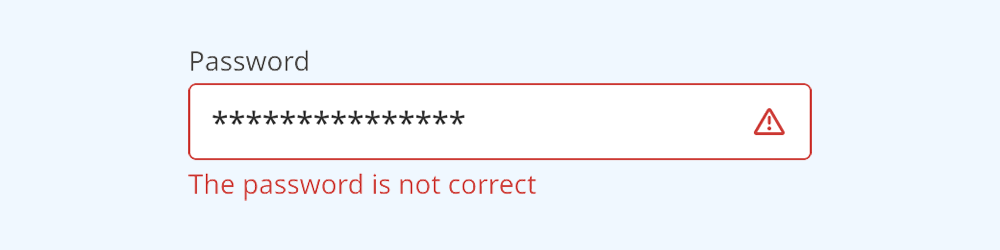
An error message can also be displayed below the description when needed.
The text field supports the following states:
- Hover
- Focused/selected
- Invalid
- Disabled
- Read-only
Behaviour
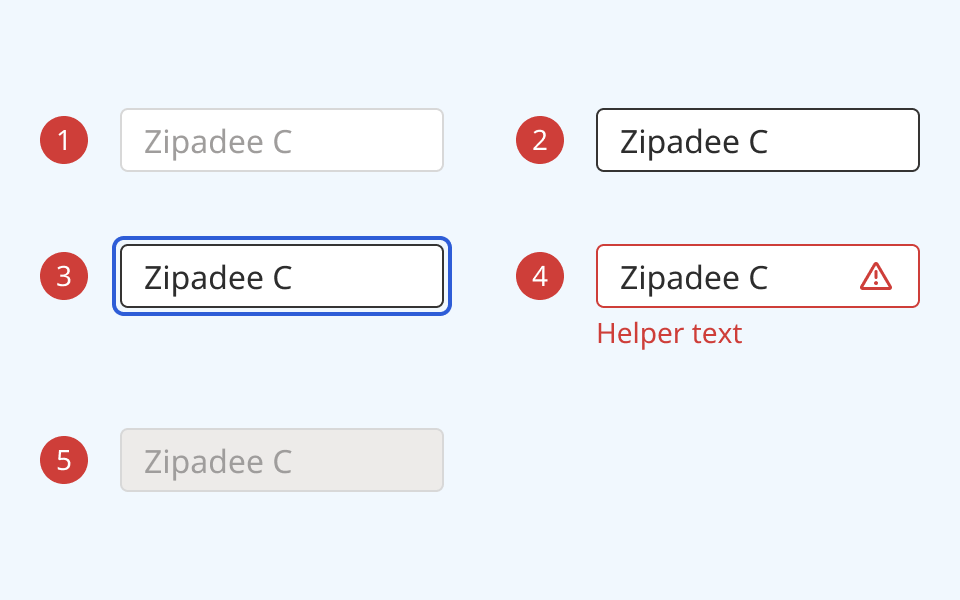
- At rest, the text field is in its default state
- On hover, the border colour and cursor visibly change
- When the text field is focused or selected:
- An offset blue focus ring appears around the input field
- A flashing cursor appears in the text field to indicate that it can accept input
- When an input is invalid:
- The border colour changes to red
- A red 'error' icon is displayed on the right side of the text field
- A red error message is rendered below the text field
- When an input is set to disabled or read-only:
- The background colour changes to grey
- A cursor indicator is shown on hover to indicate that it is disabled
- A disabled text field cannot be focused or interacted with
- A read-only field can be selected, but cannot be edited
Design guidance
Design system components are published in a Figma library. Install the library and add it to your project to start using this component.
Text fields are highly modular. All of its parts (except the input field itself) can be shown or hidden as needed, depending on your use case.
If your use case requires hiding the input label, you must also provide a non-visible label using the aria-label property.
Controls
| Control | Options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Size |
|
Toggles between the default (medium) input size and a more compact version with reduced height |
| State |
|
Toggles between different interaction states |
| Show label |
|
Toggles on/off the label above the input |
| Notification |
|
Toggles on/off the description below the input |
| Show left icon |
|
Toggles on/off an icon to the left of the input |
| Show right icon |
|
Toggles on/off an icon to the right of the input |
Technical information
Detailed technical documentation, interactive previews and code samples are published in the B.C. Design System Storybook.
A reference implementation of the text field component in React is published in the React components library. Install the package via npm to start using the component.
Events and props
The button component is a styled version of the React Aria text field component. Refer to the React Aria documentation for detailed information about:
Data validation
The text field component has built-in support for HTML constraint validation (for example, by setting a type attribute or a minimum/maximum input length) and custom validation.
You can pass custom error messages programmatically to the error message slot below the input field.
Accessibility
These summaries reflect the component used as provided. If you modify it, confirm that your changes comply with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). B.C. government digital services are required to meet the WCAG Level AA standard.
| Requirement | WCAG Success Criterion | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Make sure visual formatting is represented in the backend code | 1.3.1 (Level A) |
Label and input field are automatically associated via an aria-labelledby attribute |
| Clearly define the purpose of input fields | 1.3.5 (Level AA) |
The input has a visible label, used to explain its purpose. The input type attribute can be set to provide an additional hint. Note: if you do hide the visible label, you must use aria-label to provide a semantic label |
| Make websites keyboard accessible | 2.1.1 (Level A) |
Text field is focusable and fully operable using only the keyboard, with visual indicators for focused elements |
| Prevent keyboard navigation traps | 2.1.2 (Level A) |
When in focus, the user can exit the text field by pressing the 'Tab' key |
| Show where the keyboard is active on the screen | 2.4.7 (Level AA) |
Focus is indicated with a visible and offset secondary border around the input field |
| Make sure interaction or click targets meet a minimum size | 2.5.8 (Level AA) |
The input field has a minimum target area of 32px by 32px |
| Ensure user interface components behave predictably | 3.2.1 (Level A) |
Input value does not change and is not submitted on focus |
| Make sure components can be read and used by assistive technology | 4.1.2 (Level A) |
The input field is automatically associated to its label via an aria-labelledby attribute, and has the input role |
