Worker policies - 1.2 Hand washing
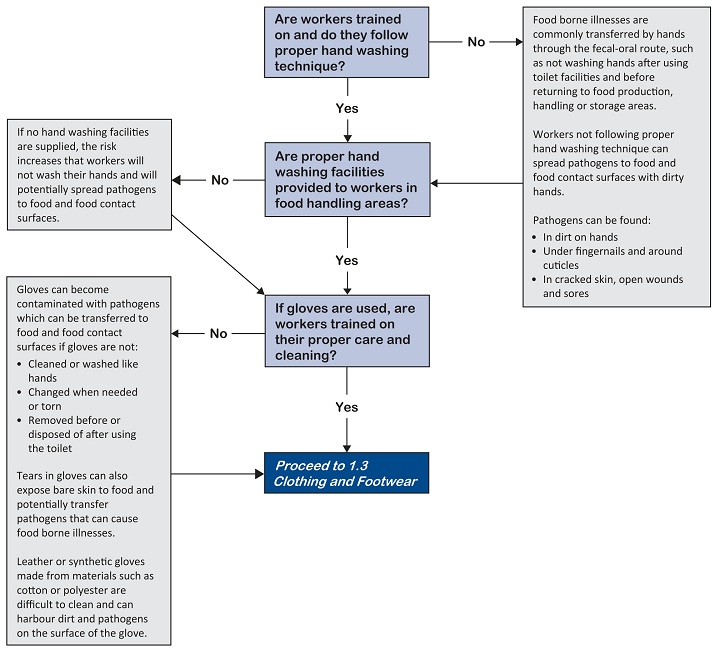
Workers can contaminate food, food contact surfaces, water supplies and packaging materials if they do not follow proper hand washing practices.
This good agricultural practice applies to farms with workers who milk livestock, handle eggs, honey, fruits or vegetables.
What needs to be done
Make sure workers use effective hand washing practices to reduce the risk of worker-borne contamination.
How to do it
Provide adequate hand washing facilities. This should include:
- Potable (safe to drink) running water
- Liquid soap
- Single-use paper towels
Make sure hands are washed often using properly maintained hand washing stations. Learn more about hand washing stations.
Establish good hand washing practices. Follow these steps for effective hand washing:
- Wet hands with potable water and apply soap
- Scrub the surface of the hands, wrists, in between fingers and under nails for 20 seconds. Fingernails should be trimmed and maintained so soil and filth can be easily removed from under and around them. If a clean nailbrush is available, use it to thoroughly remove soil from under the nails
- Rinse hands with potable water and dry with a disposable clean towel. To avoid cross-contamination, do not use common or shared towels
Make sure hands are washed:
- Before handling products, packaging materials or food contact surfaces
- Before putting on clean gloves
- Before and after breaks
- After using the toilet
- After handling garbage
- After sneezing or coughing
- After smoking
- After applying insect repellent or sunscreen
- When hands become dirty
Use sanitizers for extra protection only after washing with soap and water. Sanitizers alone are not effective in killing bacteria when hands are dirty. Dirt, moisture or oil will reduce their effectiveness.
Make sure dirty gloves don’t contaminate products. To minimize contamination, gloves should be:
- Of contrasting colour to the product being handled so that if pieces are torn off, they can be observed and removed
- Free of cuts and tears
- If disposable, discard each time hands are to be washed
- Washed or sanitized using practices similar to hand washing
Discard (throw away) gloves once they are soiled and can no longer be cleaned.
In general
- Use appropriate signage in the workplace to remind workers to wash hands frequently
- Designate someone to ensure workers are following hand washing practices, retrain as necessary
If you need an audit
Be prepared for the auditor to:
- Review written instructions and training records
- Observe hand washing practices
Laws and regulations
There are few specific agricultural laws that impact on food safety requiring persons to wash their hands on-farm. Generally, these requirements are laid out in laws regarding the processing of meat, fish and other food products or for food premises or egg-grading stations, which are outside the scope of this document.
The Milk Industry Standards Regulation, Reg. 464/81, s. 58 (2) under the Milk Industry Act requires persons to wash their hands immediately upon entering milk house before handling or touching any equipment.
