Crops - 8.2 Pesticide use
This good agricultural practice applies to all farms that apply pesticides, including products used in organic production.
Pesticides include insecticide, fungicide, bactericide, herbicide, rodenticide, miticide, molluscicide, algicide, avicide, nematicide and piscicide.
What needs to be done
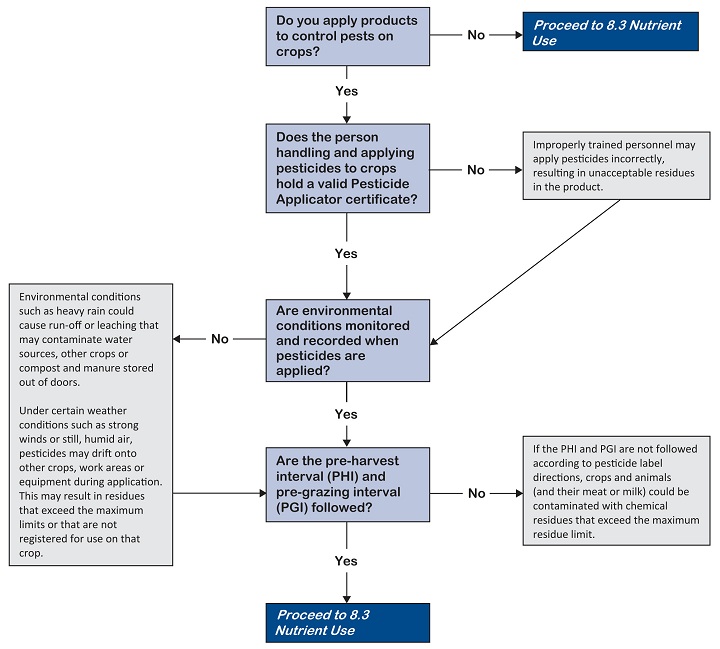
Make sure pesticides are used properly and, if required, applied by someone who holds a valid pesticide applicator certificate.
How to do it
Check the label
Use only pesticide products registered for use in Canada.
Use only for specified crops, weeds or pests as indicated on the label.
Read and follow all label directions, even if the product has been on the market for years, as application rates and usage information may change.
Apply pesticides appropriately
Make sure applications are done by a certified applicator or a custom applicator.
Apply pesticides under the right environmental conditions to reduce the possibility of spray drift, run-off or leaching that may contaminate other crops. Check the product label for details.
Maintain and calibrate the application equipment to deliver the correct rate uniformly over the field. Learn more about equipment maintenance and calibration.
Double-check calculations to make sure the application rate is the same as the rate on the label.
Clean and rinse equipment using manufacturer’s recommended procedures between applications to prevent carryover and contamination.
Follow the pre-harvest interval (PHI), pre-grazing interval (PGI), pre-slaughter interval (PSI), and milking restrictions (MR) requirements on the label. This ensures that no produce is harvested and that no animals graze on a treated field until the legal number of days after the application has passed. Failure to wait may result in residues exceeding the maximum residue limit in the crop or contamination of the milk and/or meat.
In the event that harvesting or grazing occurred before the PHI, PGI, PSI, or MR, segregate the product.
In general
If there are concerns about residues, keep the product separate and discuss options with a provincial and/or federal agricultural specialist.
Terms used in good production practice
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): The process of planning and taking steps that will prevent or manage pests.
Milking Restrictions (MR): The time that must pass between the pesticide application and milking for human consumption.
Pest Control Product Number (PCP number): The Pest Control Product Act registration number that shows that the product has been registered by Health Canada’s Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA).
Pre-grazing Interval (PGI): The time that must pass between the application of pesticides to a crop and the grazing of animals on that crop.
Pre-harvest Interval (PHI): The time that must pass between the application of pesticides to a crop and the harvesting of that crop.
Pre-slaughter Interval (PSI): The time that must pass between the pesticide application and slaughter of animals.
Records to keep
Use the Pesticide use record (PDF) or your own record that includes:
- Application date and time of completion
- Chemical applied (with PCP number)
- Rate applied
- Weather conditions (e.g. temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and direction)
- Crop and stage of growth
- Target pest(s)
- Field identification, location and size of treated area
- Earliest possible harvesting/grazing date
- Initials (and certification number if contracted out) of the person applying the pesticide
If you have an audit
Be prepared for the auditor to review:
- Pesticide use records
- A valid pesticide applicator certificate and/or license
Laws and regulations
All pesticides used on-farm must be registered for the specific use in Canada, and must be used according to federal and provincial legislation. The laws include the Integrated Pest Management Act, S.B.C. 2003, c. 58, Integrated Pest Management Regulation Reg. 604/04, and the Hazardous Products Act (Canada), R.S. 1985, c. H-3.
Pesticides must not contaminate foods that are listed in the Food and Drugs Act (Canada), R.S. 1985, c. F-27, Food and Drug Regulations, Division 15. Under the Food Safety Act and Meat Inspection Regulation, Reg. 349/2004, s. 10, food animals are inspected against the standards related to food safety and animal health established under the Food and Drugs Act (Canada) and the Meat Inspection Act (Canada).
The pesticide product label is a legal document that specifies restrictions on use (rates, withdrawal periods, re-entry requirements, days to harvest, buffer zones, protective equipment, and environmental protection practices). The Integrated Pest Management Act, S.B.C. 2003, c. 58, s. 3 (1) and the Integrated Pest Management Regulation, Reg. 604/04, s. 46 (3) (a) specify that no person shall use a pesticide except in accordance with the label for that pesticide or this Regulation.
The Integrated Pest Management Act and Integrated Pest Management Regulation, Reg. 604/04, s. 28 (1) sets out requirements for notification and posting when pesticides are used.
