Livestock and poultry - 9.2 Bedding use
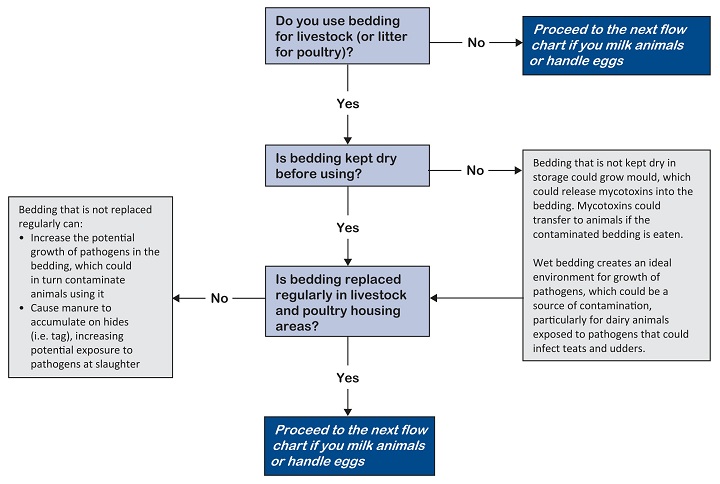
Wet bedding can cause manure accumulation on livestock and poultry and act as an ideal environment for biological contamination.
This good agricultural practice applies to all farms. Some examples of bedding are:
- Hay
- Sand
- Shredded paper
- Sawdust
- Straw
- Wood chips
- Wood shavings
Avoid cedar wood products as they secrete toxins which can cause udder health problems and skin irritations.
What needs to be done
Maintain bedding to create an environment that does not promote contamination of livestock and poultry by biological agents.
How to do it
Keep the housing area as dry as possible:
- Control barn temperature and humidity
- Maintain proper ventilation to prevent condensation and promote drying
- Repair water leaks, for example, leaking water bowls, taps and building eaves
- Replace bedding and manure as needed
- Avoid using mouldy bedding, as moulds can be a source of mycotoxins
- Do not use sawdust or shavings derived from treated wood or cedar wood
If you have an audit
Be prepared for the auditor to:
- Review vendor assurance that purchased bedding is free from treated wood products
- Visually observe the housing environment for adequate, clean and dry bedding