Dry Bulb Onions

Growing dry bulb onions
Varieties
Fall-seeded (trial)
Walla Walla (sweet).
Spring-seeded
Yellow (cooking)
Frontier, Copra, Tamara, Talon, Milestone, Highlander, Mountaineer.
Yellow (Spanish)
Early (trial): Brahma, Cima, Yula, Early Shipper, Golden Cascade, Magnum, Pinnacle, Zenith.
Red
Red Beauty, Red Bull, Salsa.
See your seed dealer for the most recent variety recommendations.
Soil temperature
The minimum temperature for germination is 9°C. The optimum range is 16 to 24 °C.
Soils
Peat or muck soils are preferred, but good crops are grown on silt loams and sandy loams.
Seed treatment
See Onion Smut under the Dry Bulb Onion Disease Management section of this page.
For control of Pythium damping off, use seed treated with Apron XL LS seed protectant.
Seeding and transplanting
Over-wintered onions
Direct-seeded
Seed with a precision seeder as described for spring-seeded onions. Normal seeding date is August 15 to 20.
Seed-beds for transplant production
Usually done the first week of August. Sow 2.75 kg seed for each hectare (1.1 kg/acre) to be set, approximately 35 kg/ha (14 kg/acre) of seed-bed. One hectare of seed-bed will produce enough transplants for 12 hectares of onions. Seed is drilled to a depth of 2.5 cm or slightly less.
Seed may be drilled with a wide shoe attachment which scatters the seed over a 10 cm band in rows with 40 cm centres. The second method is to use a tractor-drawn gang drill which drops the seed thickly in rows 5 to 7.5 cm apart. This results in solid beds with widths depending on tractor wheel settings.
The third method is to drill the seed thickly in single rows 20 to 22 cm apart. In the spring the plants in every other row are lifted and used for transplants. The remaining rows are thinned by hand, leaving a plant every 7.5 cm for a crop. In the Southern Interior, light sprinkler irrigation following the seeding will often be necessary to obtain a satisfactory stand.
In the spring, loosen plants before pulling and tie in bundles of 100 to 200. If being moved any distance, or if transplanting will be delayed, store at 0 to 2°C with relative humidity of 90%. Immediately before planting, trim the plants to leave 1.5 cm of the original root and 10 cm of the green top. Set in rows 40 cm apart, with 6 to 7.5 cm between plants.
Spring-seeded onions
Onions may be seeded as soon as the land can be made ready, but mid-April is considered ideal. Seeding should be completed by May 1. Approximately 3.25 kg raw seed per ha (1.3 kg/acre) is required. For precision seeding see next paragraph. When using the Planet Junior drill with 10 cm scatter shoe, the drills should be set to drop 11 seeds per 25 cm of row 2 to 2.5 cm deep. Row spacing is usually 4 rows per bed on 1.8 m centres.
Precision seeding
This method of placing individual seeds at a predetermined spacing within a row produces a crop of more uniform size, less culls and higher yield. Use coated seed and sow two lines 7.5 cm apart per row with 12 seeds per 25 cm of row. Row spacing is usually 4 rows on 1.8 m beds.
With normal coating and spacing approximately 18 kg/ha (7 kg/acre) of seed will be required. This results in a population of approximately 925,000 plants/ha (370,000 plants/acre). See “Precision Seeding” section of the Vegetable Production Guide: Planting (PDF, 190KB).
Irrigation
Onions are shallow-rooted, and unless their moisture supply is constant, they will “bulb out” early and the resulting sizes may be small. Four or five irrigations per season are usually required. Irrigation should be discontinued after the first week in August to encourage crop maturity and limit disease development.
Fertilizer
A soil test is necessary to determine phosphate and potash requirements. Use the Vegetable Production Guide: Nutrient Management (PDF, 310KB) for recommendations based on soil test results.
Coastal area (muck soil)
Where no manure has been applied, broadcast and disc in 70 kg/ha (28 kg/acre) nitrogen and all of the required potash and phosphate.
Interior of B.C.
Where no manure has been applied, broadcast and disc in 90 kg/ha (36 kg/acre) nitrogen and all the required phosphate and potash.
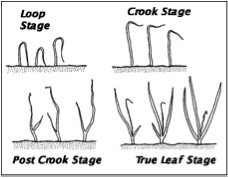
Onion growth stages
Harvesting, curing and storage
Dig when two-thirds of the tops are down, and cure by windrowing in the field if weather conditions are favourable. Running them up and over a potato digger a few days after digging will shorten the drying period. This should be done after each rainfall. Under wet conditions or after field drying has occurred, the onions should be placed in storage sheds. Under wet conditions the height of the onion pile should not exceed 3 m.
Curing is completed or accomplished by forcing air of a lower relative humidity than the air inside the storage through the bottom of the onion pile to the top; one and one-half cubic metres of air per minute for each cubic metre of onions is recommended. If the weather is cool and wet, forced air at 24 to 30°C and 70% relative humidity is recommended.
If the onions are also wet, forced air at 30°C and a relative humidity of less than 70%, should be used as soon as loading is completed. This should be continued until the outer skins and neck are dry. Then the crop should be allowed to cool gradually by slowly reducing the temperature to that of the outside air (0°C and above). After curing, the relative humidity in the storage should be maintained between 60 and 70%.
The less fluctuation the better. During dry, cold weather (above 0°C) the vents may be opened and the fans used to circulate cold outside air throughout the pile. During wet or very cold weather (below 0°C) the building should remain closed and the air within should be re-circulated periodically.
Dry bulb onion weed management
Stale seedbed
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Ignite 15 SN(glufosinate ammonium)Group 10 |
2.7 to 5.0 L/ha (1.1 to 2.0 L/acre) Apply in 110 to 330 L/ha (45 to 135 L/acre) of water at 275 to 310 kPa |
N/A |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
Pre-emergence
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Chateau(flumioxazin)Group 14 |
140 g/ha (57 g/acre) Transplanted onions: 2- to 6- leaf stage Direct seed onions: 3- to 6- leaf stage |
45 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
Post-emergence
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Centurion/Select(clethodim) Group 1 |
0.19 to 0.38 L/ha (77 to 154 mL/acre Apply in 55 to 225 L/ha (22 to 90 L/acre) of water at 275 kPa |
45 |
|
Poast Ultra(sethoxydim) Group 1 Note: No longer produced |
Annual grasses (incl. volunteer cereals): 320 mL/ha (130 mL/ac) Annual grasses & quackgrass suppression: 470 mL/ha (190 mL/ac) Quackgrass: 1.1 L/ha (445 mL/ac) |
50 |
|
Excel Super(fenoxaprop-pethyl)Group 1 |
670 mL/ha (270 mL/acre) Apply in at least 110 L/ha (45 L/acre) water at 275 kPa |
38 |
|
Venture L(fluazifop-P-butyl & S-isomer)Group 1 |
barnyard grass (2-5 leaf stage): 0.8 L/ha (0.32 L/acre) proso millet (2-5 leaf): 1.0 L/ha (0.4 L/acre) foxtails (2-4 leaf): 1.4 L/ha (0.56 L/acre) quackgrass (3-5 leaf): 2.0 L/ha (0.8 L/acre) |
42
42
42
60 |
|
Prowl H2O(pendimethalin) |
Muck soils:
6.6 L/ha (2.7 L/acre) Mineral soils: 2.42 L/ha (1 L/acre) Apply in 250 L/ha (100 L/acre) of water at 138 to 276 kPa.
|
N/A |
Muck soils:
Mineral soils:
All soils:
|
Pardner(bromoxynil)Group 6 |
500 mL/ha (200 mL/acre) |
75 |
|
Bromotril 240 EC(bromoxynil)Group 6 |
600 mL/ha (250 mL/acre) |
75 |
|
Aim EC(carfentrazone-ethyl) Group 14 |
37 to 117 mL/ha (15 to 47 mL/acre) Apply in 100 L/ha (40 L/acre) of water |
1 |
|
Goal 2XL(oxyfluorfen)Group 14 |
Onions (2 true leaves): Weeds (2 – 4 leaf stage): 500 mL/ha (200 mL/acre) Apply in 500 L/ha (200 L/acre) of water at 275 kPa |
56 |
|
Frontier Max(dimethenamid -P)Group 15 |
1.29 L/ha Apply using 200 to 300 kPa spray pressure. |
60 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
Dry bulb onion insect management
Leafminer
Please refer to the Vegetable Production Guide: Pest Management (PDF, 1.2 MB) for guidance on controlling leafminers.
Onion maggot
Small, grayish fly, smaller than a house fly, lays eggs at base of plants. Small, white maggots feed in onion bulbs. If attack occurs early, plants may be killed. If attacked later, plants live, but the bulbs are misshapen and contain maggots. Secondary rot often occurs.
Monitoring
Monitoring with white sticky traps is useful to detect both onion maggot flies and onion thrips. With this information, control can be achieved with fewer sprays. Onion flies, however, cannot be properly identified without the use of a dissecting microscope and considerable expertise. Commercial scouting services are recommended for accurate identification.
Control
Cull piles should be removed to the dump or buried to prevent onion fly breeding and subsequent field infestation.
Dry bulb onions (including silverskins) grown from seed
A combination of furrow and foliage or foliage treatments alone are required.
Furrow treatment for maggot control
Currently, there are no products registered for furrow treatment for onion maggot control.
Foliage treatments
If the furrow treatments are not used, apply sprays at 7 to 10 day intervals beginning after seedling emergence, but no earlier than April 15. For crops planted in late April or May, the first spray should be applied 4 days after seeding. Spraying should begin four weeks after planting with a furrow treatment. In all cases, spraying should continue until July 15.
Note: If your fields are being monitored for onion flies, follow spray recommendations of the person who does the monitoring.
Spraying of weeds immediately surrounding onion fields will give additional protection against the onion maggot. Caution: Do not spray headland areas where water may become contaminated. Sprays are most effective when applied in the morning (8 to 10 a.m.) or early evening (6 to 9 p.m.). Use sufficient water to thoroughly wet plants and soil. Try to achieve a very narrow band over the row. If maggots become bigger than 2 or 3 instars, a spray will not be effective but should control future emergence. To deter insects from developing resistance, alternate sprays between the two groups listed in the table below.
Sets, multipliers, and transplants
Use the furrow and foliage treatments or the foliage treatments alone, as given above and in the table below.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Dibrom(naled)
Group 1B |
530 mL/ha (215 mL/acre) Apply in 100 to 300 L/ha (40 to 120 L/acre) of water |
4 |
|
Mako(cypermethrin)
Group 3
|
175 mL/ha Apply in 110 L/ha (44 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Up-Cyde 2.5 EC(cypermethrin)
Group 3
|
280 mL//ha Apply in 100 to 500 L/ha (40 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Scorpio Ant and Insect Bait(spinosad) Group 5 |
25 to 50 kg//ha |
3 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
Thrips
Very tiny (1 mm), thin, black, brown or yellowish, active insects causing silvering of the leaves. Black fecal spots can be seen where thrips are feeding. When severe, entire plant may wilt and die. Damage may resemble Botrytis (see below).
Control
When thrips are present, using sufficient water to provide good coverage, spray three times at 10 day intervals beginning the third week of June with:
Dibrom at the rates and days to harvest restrictions given under Foliage Treatments for Maggot Control. See table below for other products.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Dibrom(naled)Group 1B |
530 mL/ha (215 mL/acre) Apply in 100 to 300 L/ha (40 to 120 L/acre) of water. |
4 |
|
Mako(cypermethrin)
Group 3
|
175 mL/ha Apply in 100 to 500 L/ha (40 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Up-Cyde 2.5 EC(cypermethrin)
Group 3
|
280 mL//ha Apply in 100 to 500 L/ha (40 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Decis 5 EC(deltamethrin)
Group 3 |
200 mL/ha (80 mL/acre) Apply in 200 to 500 L/ha (80 to 200 L/acre) water |
5 |
|
Malathion 85E(malathion)
Group 1B |
1.1 L/ha
(0.44 L/acre) Apply in 1000 L/ha (405 L/acre) of water
|
3 |
|
Delegate WG(spinetoram)
Group 5 |
200 to 336 g/ha Apply in 300 to 500 L/ha (120 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Entrust 80(spinosad)
Group 5
Used in organics
|
131 to 158 g/ha Apply in 300 to 500 L/ha (120 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Entrust SC(spinosad) Group 5 Used in organics |
437 to 527 mL/ha (177 to 213 mL/acre) Apply in 300 to 500 L/ha (120 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Success(spinosad)
Group 5
|
218 to 262 mL/ha Apply in 300 to 500 L/ha (120 to 200 L/acre) of water |
3 |
|
Movento 240 SC(spirotetramat)
Group 23 |
365 mL/ha |
3 |
|
Agri-Mek 1.9% EC(abamectin)
Group 6 |
600 to 1200 mL/ha Apply in 200 L/ha (80L/acre) of water |
30 |
|
Agri-Mek SC(abamectin)
Group 6
|
135 to 270 mL/ha Apply in 200 L/ha (80L/acre) of water |
30 |
|
Exirel(cyantraniliprole)
Group 28
|
1000 to 1500 mL/ha Apply in 200 L/ha (80 L/acre) of water |
1 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
OMRI-USA = Organic Materials Review Institute of USA
OMRI-Canada = Organic Materials Review Institute of Canada
Dry bulb onion disease management
Botrytis blast or leaf blight
Small white spots appear on leaves later coalescing into elongated blotches. May look like thrips damage. Grey mould may appear on the dead tissue under wet conditions.
Control
- Avoid high rates of seeding as dense crops are most severely affected.
- Avoid high rates of nitrogen fertilizer.
- Avoid sprinkler irrigation if blast is apparent.
- See table below for registered products.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Bravo 720(chlorothalonil)Group M5 |
1.7 to 3.3 L/ha |
7 |
|
Bravo ZN(chlorothalonil)
Group M5
|
2.4 to 4.8 L/ha (1.0 to 1.9 L/acre) |
7 |
|
Bravo ZNC(chlorothalonil)
Group M5
|
|||
Echo 720(chlorothalonil)
Group M5
|
1.7 to 3.3 L/ha (0.7 to 1.3 L/acre) |
7 |
|
Dithane
|
2.25 kg/ha (0.9 kg/ acre) |
14 |
|
Penncozeb 75DF(mancozeb)
Group M
|
2.25 to 3.25 kg/ha (0.9 to 1.3 kg/acre) |
10 |
|
Penncozeb 75DF Raincoat(mancozeb)
Group M
|
2.25 kg/ha (0.9 /acre) |
14 |
|
Zineb 80 W(zineb) Group M |
0.85 to 3.3 kg/ha Apply in 1000 to 1500 L/ha (405 to 605 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Cueva(copper octanoate)
Group M1
Used in organics
|
Use a 0.5% to 2% solution at 470 to 940 L/ha (190 to 380 L/acre) | 1 |
|
Lance WDG(boscalid)
Group 7 |
475 g/ha (190 g/acres) Apply in 100 L/ha (40 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Sercadis(fluxapyroxad)
Group 7 |
333 to 666 mL/ha (135 to 270 mL/acre) Apply in 100 L/ha (40 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Miravis Duo(pydiflumetofen & difenoconazole) Group 7 & 3 |
1.0 L/ha (405 mL/ac) Apply in 150 L/ha (60 L/ac) of water |
7 |
|
Switch 62.5 WG(cyprodinil & fludioxonil)
Group 9 & 12 |
775 to 975 g/ha (314 to 395 g/acre) Apply in 200 L/ha (80 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Scala SC(pyrimethanil)
Group 9 |
1.0 L/ha (400 mL/acre) Apply in 300 L/ha (120 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Acapela(picoxystrobin) Group 11 |
0.6 to 0.88 L/ha Apply in 110 L/ha (45 L/ac) of water |
0 |
|
Pristine WG(boscalid & pyraclostrobin)
Group 7 & 11 |
1000 to 1300 g/ ha (405 to 525 g/acre) |
7 |
|
Allegro 500 F(fluazinam)
Group 29 |
1.16 L/ha (470 mL/acre) Apply in 100 L/ha (40 L/acre) |
7 |
|
Serenade Opti(Bacillus subtilis)
Used in organics
|
Leaf Blight: 1.7 to 2.5 kg/ha (700 to 1000 g/acre) |
0 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
OMRI-Canada = Organic Materials Review Institute of Canada
Botrytis neck rot
Rot usually begins in the neck. Rotted tissues become water-soaked and soft. A grey mould develops on the surface, later containing hard, black sclerotia. It affects bulbs during curing and storage.
Control
- Grow early-maturing tight-necked varieties.
- Do not irrigate after the first week in August.
- Dig bulbs when two-thirds of the tops are down.
- Dry thoroughly for 8 to 18 days. Artificial drying may be necessary in wetter than normal season.
- Store in well-ventilated storage at 0 to 4°C, with low humidity of 70%.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Serenade Opti(Bacillus subtilis)
Used in organics
|
(700 to 1000 g/acre) | 0 |
|
Acapela(picoxystrobin) Group 11 |
0.44 to 0.88 L/ha Apply in 110 L/ha (45 L/ac) of water |
0 |
|
Scala SC(pyrimethanil)
Group 9 |
1.0 L/ha (400 mL/acre) Apply in 300 L/ha (120 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Gavel DF(mancozeb/zoxamide) Group M3 & 22 |
1.7 to 2.25 kg (690 to 900 g/acre) |
14 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
Downy mildew
(Pernospora)
This fungus, which overwinters in bulbs, first appears as yellowish spots on the upper halves of leaves which are later covered by a purplish, fuzzy mildew. The disease increases rapidly under conditions of high humidity.
Control
- Practice sanitation and rotation. Cull piles with onions growing on them are an important source of inoculum.
- Avoid planting spring-seeded onions near overwintering onions or near onions grown from sets.
- Keep cultivations to a minimum and cultivate preferably when the leaves are dry.
- Spray every 7 to 14 days commencing June 1 for transplanted crops, and June 15 for spring-seeded crops, or when you are advised by your field scout. Add a spreader to obtain good coverage. Use the products listed in the table below.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Serenade Opti(Bacillus subtilis)
Used in organics
|
1.7 to 3.3 kg/ha (700 to 1300 g/acre) |
0 |
|
Cueva(copper octanoate) Group M1 Used in organics |
Use a 0.5% to 2% solution at 470 to 940 L/ha (190 to 380 L/acre) |
1
|
|
Copper oxychloride 50(copper oxychloride)
Group M2 |
3.0 kg/ha Apply in 500 L/ha (200 L/acre) of water |
2 |
|
Zineb 80 W(zineb)
Group M
|
0.85 to 3.3 kg/ha Apply in 1000 to 1500 L/ha (405 to 605 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Ridomil Gold MZ 68WG(metalaxyl-M & S-isomer/mancozeb) Group 4 & M3 |
2.5 kg/ha (1.0 kg/ac) Use sufficient water to ensure thorough coverage at 275 kPa |
14 |
|
Pristine WG(boscalid & pyraclostrobin)
Group 7 & 11 |
1000 to 1300 g/ ha (405 to 525 g/acre) |
7 |
|
Reason 500SC(fenamidone)
Group 11 |
400 mL/ha (160 mL/acre) |
7 |
|
Cabrio EG(pyraclostrobin)
Group 11 |
560 to 840 g/ha (220 to 340 g/acre) Apply in 225 L/ha (90 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Quadris Top(azoxystrobin/ difenoconazole)
Group 11 & 3
|
710 to 1000 mL/ha Apply in 150 L/ha (60 L/acre) of water. |
7 |
|
Torrent 400SC(cyazofamid)
Group 21
|
0.20 L/ha (80 mL/acre) Apply in 200 to 600 L/ha (80 to 240 L/acre) of water. |
0 |
|
Gavel DF(mancozeb/zoxamide)
Group M3 & 22
|
1.7 to 2.25 kg (690 to 900 g/acre) | 14 |
|
Aliette WDG(fosetyl-aluminum)
Group 33 |
2.8 kg/ha Apply in 150 L/ha (60 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Phostrol(mono- and dibasic sodium, potassium, and ammonium phosphites)
Group 33
|
2.9 to 4.3 L/ha (1.2 to 1.7 L/acre)
Apply in 225 L/ha (90 L/acre) of water.
|
0 |
|
Revus(mandipropamid)
Group 40 |
400 mL/ha (160 mL/acre) Apply in 100 L/ha (40 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Forum(dimethomorph)
Group 40
|
450 mL/ha Apply in 200 L/ha (80 L/acre) of water. |
0 |
|
Zampro(ametoctradin & dimethomorph)
Group 40 & 45
|
1.0 L/ha Apply in 200 L/ha (80 L/acre) of water. |
0 |
|
Orondis Ultra(oxathiapiprolin & mandipropamid)
Group 49 &40
|
0.4 L/ha Apply in 100 L/ha (40 L/acre) of water. |
7 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
OMRI-Canada = Organic Materials Review Institute of Canada
Fusarium basal rot
Plants appear stunted and lopsided. Bulbs have soft, mealy decay at base or on one side. Rot continues in storage.
Control
- Control onion-maggot.
- Follow four-year crop rotation with non-susceptible crops such as carrots, celery, lettuce and beets.
- Avoid root and bulb injury during cultivation.
- During storage and transit, keep temperature below 4°C.
- Use only disease-free sets. This is especially important on new land or after rotation, so as to avoid contamination.
Onion smut
Powdery brown to black, elongated blisters develop within the cotyledons, leaves and scales of seedling plants; most affected seedlings die while young; some persist and lesions may occur on mature bulbs.
Control
In fields with a minor smut problem, the Pro-Gro seed treatment or Thiram granular treatments may be adequate. The infection period for smut is relatively short from about the second day after germination until the seedling is in its first leaf. It is critical that the seed and seedling be protected through this period. Use at least one of the following:
Pro-Gro seed treatment at the rate of 25 g/kg of seed. Apply to Methocel-treated seed before any other insecticide, fungicide or coating is added:
Preparation and application of the sticker
- Sprinkle Methocel A15 in water at the rate of 50 g/L to make up a 2% solution. Do not stir. Let stand overnight or longer in a cold area until the material is dissolved.
- Place the seed in a container which can be rotated or shaken and slowly add 60 mL of the 2% solution per kilogram of seed. Mix until the seed is uniformly coated and shining. If necessary, add more of the solution, until this condition is achieved.
Application of fungicide for smut control
Slowly add Pro Gro at the rate of 25 g/kg of seed. Mix well to ensure even distribution. Do not mix with bare hands.
Other control methods
- Set out healthy transplants (smut does not infect transplants);
- Seed fields with a previous history of smut as late as possible as there will be less infection under conditions favourable to rapid seed germination and seedling growth.
- See table below for registered products.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Dithane
|
4.4 to 8.8 kg/ha (1.8 to 3.5 kg/acre) |
100 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
Pink root
(Phoma)
This is a soil-borne fungal disease. Infected roots become pink and die. Plants appear to be nutrient deficient. The disease can appear at any time of plant development, from seedling stage to maturity.
Control
No satisfactory control measure is known, but the following are good general recommendations:
- Rotate with lettuce, celery, beets, potatoes, rutabagas or other crops unrelated to onions. The fungus will survive on cereals grown in rotation.
- Do not plant onions in severely infested land.
- Ensure rapid bulb growth by the use of adequate fertilizer, irrigation, cultivation, cover crops, etc.
- Do not plant infected plants.
- Soil fumigation is effective on sandy but not on muck soils.
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Serenade Soil(QST 713 strain of dried Bacillus subtilis)
Used in organics
|
2.7 to 14 L/ha (1.1 to 5.7 L/acre) | 0 |
Surface Application:
Post-plant applications:
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
OMRI-Canada = Organic Materials Review Institute of Canada
White rot
(Sclerotium cepivorum)
This serious disease is now well established in the Southern Interior, Cloverdale and Burnaby onion-growing areas. Infected plants show yellowing and die-back of the leaf tips, progressing downward to the roots. Bulbs develop watery decay, eventually covered with white, fluffy, fungus growth dotted with masses of small black sclerotia.
Control
Once established in a field, white rot builds up whenever onion or garlic is grown. The sclerotia can persist in the soil for 10 years or more. Control is difficult and costly, so utmost precautions should be taken to prevent spread into new fields. Avoid growing onions in fields known to be infested if at all possible. Wash down equipment in a safe area when moving from an infested to a clean field. Dispose of diseased onions, trash and containers in such a way as to minimize the chances of contaminating new areas. Take steps to reduce the danger of flood waters carrying diseased onions and sclerotia from field to field. It is especially important to avoid contaminating clean land with infected transplants or sets which were grown on infested land.
Sprout inhibition
Sprout inhibition will extend the storage period and, therefore the selling period for storage onions. Use Royal MH 30 XTRA (maleic hydrazide) at 8.36 L/ha (3.4 L/acre) in a minimum of 300 L/ha (120 L/acre) water by ground equipment. Necessary conditions for best results are:
- A uniform or even-growth crop.
- 50% of the tops down, and all tops with at least 5 to 8 green leaves. This condition usually occurs about 10 days to two weeks before harvest time.
- No rain or irrigation for 24 hours after application.
- Plants should be healthy and reasonably free of insect or disease damage.
- Use on storage varieties. Royal MH 30 XTRA will not make a poor-keeping variety into a storage variety.
- Do not spray too early as spongy hollow-necked bulbs may result.
- Spray during early morning or on cloudy days.
- Apply at temperatures below 25 °C.
- Observe a 10 day pre-harvest interval.
Suppression of Stemphylium leaf blight
| Product | Rate | PHI* | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Aprovia(benzovindiflupyr)
Group 7 |
750 mL/ha (300 mL/acre) Apply in at least 150 to 600 L/ha (60 to 240 L/acre) of water |
7 |
|
Miravis Duo(pydiflumetofen & difenoconazole) Group 7 & 3 |
1.0 L/ha (405 mL/ac) Apply in 150 L/ha (60 L/ac) of water |
7 |
|
*PHI = Pre-harvest interval
BUFFERS – Refer to product label for buffer requirements, and consult the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Regulations and Safety (PDF, 421KB)
PESTICIDE GROUP DETAILS – see the Vegetable Production Guide: Pesticide Toxicity Table (PDF, 703KB)
